The integration of VR training in healthcare represents a transformative leap in medical education, addressing the pressing need for more effective and engaging training methodologies. According to a report by the Journal of Medical Internet Research, immersive technologies like virtual reality have the potential to enhance medical training outcomes by up to 40% when compared to traditional methods. As the complexity of medical procedures and the demands for skilled professionals continue to rise—projected to reach a global shortfall of 18 million healthcare workers by 2030—the adoption of innovative VR training solutions is becoming increasingly vital.

Virtual reality (VR) is revolutionizing the landscape of medical training by offering immersive experiences that were previously unattainable. Traditional methods often involve textbooks, lectures, and limited hands-on practice, which can leave students unprepared for real-life medical scenarios. With VR, trainees can engage in realistic simulations that recreate a variety of clinical environments and patient interactions. This interactive approach not only enhances learning retention but also builds confidence as students practice procedures and decision-making skills in a safe, controlled setting.
Moreover, VR technology allows for personalized education tailored to individual learning paces and styles. Medical students can repeat simulations as many times as needed until they feel proficient, thus mastering complex procedures before working with actual patients. The ability to analyze performance metrics during these VR sessions further aids educators in identifying areas where a student might need additional support. As the healthcare field continues to evolve, incorporating VR into medical training promises to equip future healthcare professionals with the necessary skills and experience to deliver superior patient care.
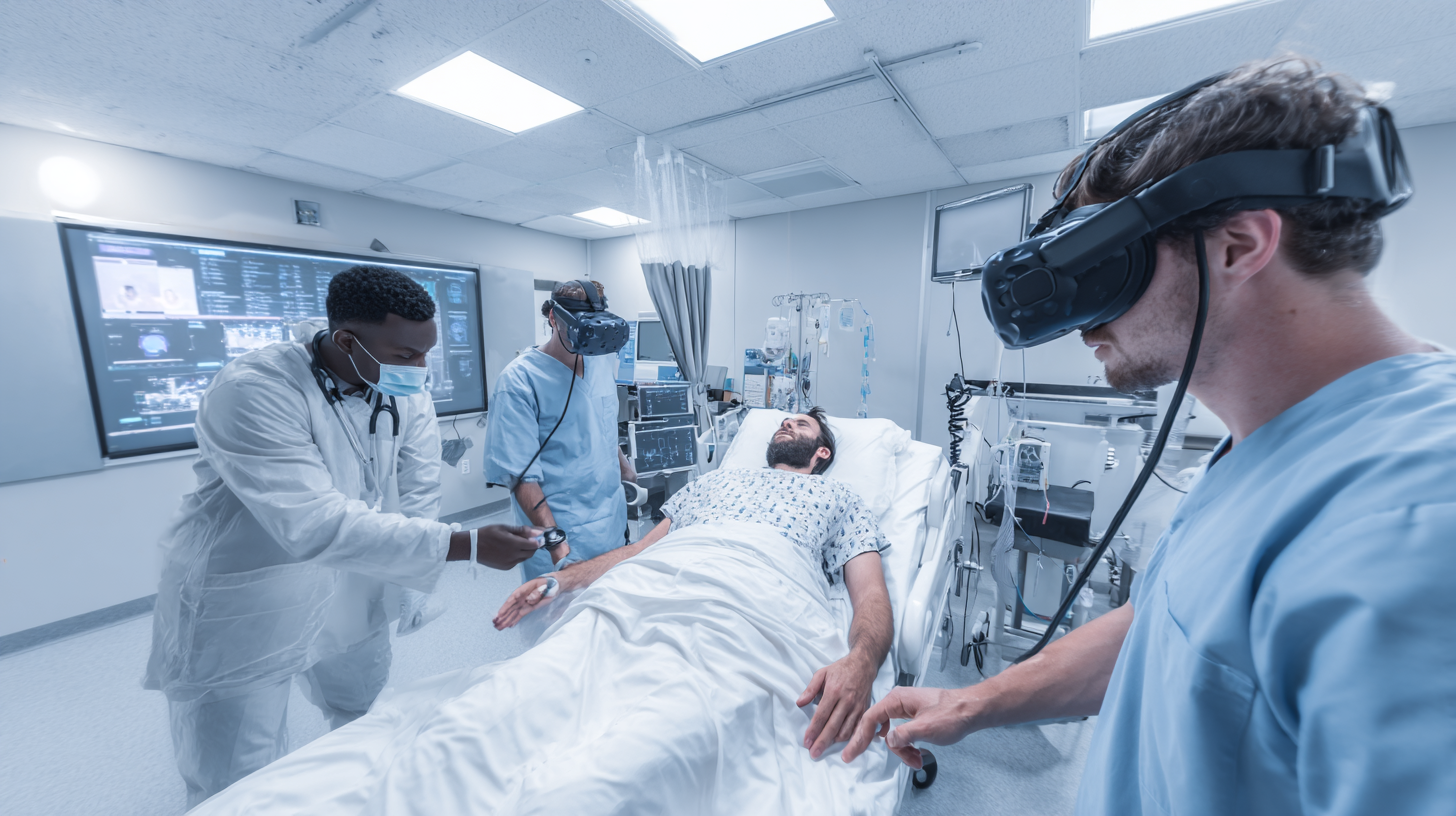
 Innovative VR Solutions: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Practice in Healthcare
Innovative VR Solutions: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Practice in Healthcare
The integration of Virtual Reality (VR) solutions in medical education is revolutionizing the way healthcare professionals are trained. According to a report by the National Center for Biotechnology Information, approximately 80% of medical students feel that traditional teaching methods fail to prepare them adequately for real-life clinical situations. VR technology addresses this gap by providing immersive, hands-on experiences that enhance understanding and retention of complex medical concepts. Studies indicate that training with VR simulations can improve procedural skills by up to 50%, allowing for a more effective learning process.
Tips for leveraging VR in medical education include encouraging collaborative learning environments where students can interact and solve problems together in a virtual setting. Institutions should also invest in up-to-date VR equipment and software, as continual advancements in technology can provide more realistic simulations and engaging scenarios. Further, it is essential to assess the effectiveness of VR training through feedback and performance metrics to ensure it meets educational goals.
As the demand for skilled healthcare professionals grows—projected to reach a global shortage of 18 million by 2030—implementing innovative VR solutions in medical curricula can be a pivotal strategy in preparing a competent workforce. By bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, VR has the potential to transform the landscape of medical education for future generations.
As medical education continues to evolve, immersive learning environments created through virtual reality (VR) are becoming increasingly vital for both students and professionals. These innovative solutions offer a unique opportunity to experience clinical scenarios in a safe and controlled setting, enhancing critical decision-making skills and procedural competencies. By simulating real-world situations, VR training allows learners to practice without the inherent risks associated with live patients, thus building confidence and improving the overall quality of patient care.
**Tips for Maximizing VR Training Benefits**: To make the most of VR training, learners should actively engage with the simulations, reflecting on their performance and seeking feedback. Incorporating VR sessions into a regular study routine can also reinforce learned concepts, making them more memorable. Furthermore, collaborating with peers during VR training can foster discussions about best practices and troubleshooting common challenges, which enriches the overall learning experience.
The immersive nature of VR goes beyond just skill acquisition; it also enhances empathy and understanding of patient experiences. By stepping into the shoes of patients, medical professionals can develop a deeper connection to the human side of medicine, which is essential for effective healthcare. This holistic approach not only prepares students better for real-life situations but also reinforces the importance of compassion in the medical field.
The integration of virtual reality (VR) in medical education presents significant promise but is not without its challenges and limitations. A recent report by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) highlights that while 70% of medical schools are exploring innovative teaching technologies, only 20% have fully implemented VR solutions into their curricula. This disparity stems from high costs of development and deployment, which can reach up to $1 million per program, making it a daunting investment for many institutions.
Moreover, the variability in technological proficiency among educators further complicates the adoption of VR training. A survey conducted by the Medical Education Technology Association (META) indicated that nearly 40% of faculty members lack confidence in utilizing VR tools effectively. This skills gap can hinder the potential benefits of immersive learning experiences, ultimately affecting student engagement and competency development. Additionally, the challenge of ensuring content validity and aligning VR scenarios with actual clinical practices remains a crucial concern, as only 32% of VR-based simulations currently meet accreditation standards as per the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME).
With these barriers in mind, medical institutions must navigate the dual task of upgrading technological infrastructure and enhancing educator training to realize the full potential of VR in transforming medical education.
This chart illustrates the key challenges faced during the implementation of VR training solutions in medical education, including cost, technology integration, and user acceptance.
The integration of virtual reality (VR) technologies in health sciences training marks a significant shift in medical education. As VR platforms become more sophisticated and accessible, they enable immersive learning experiences that mimic real-life scenarios. This evolution not only enhances the engagement of students but also prepares them with hands-on skills that are crucial for patient care. Recent studies using advanced natural language processing techniques, such as BERTopic, have analyzed the thematic trends in VR research, revealing a growing interest in its applications across various disciplines, including nursing education and therapy.
Tips: When exploring VR training solutions, consider platforms that incorporate AI-driven haptics, which can replicate the feel of real-life medical procedures. This technology is essential for hands-on training and can significantly boost retention and skill competency among students.
Moreover, the adaptability of VR technology allows for continuous updates and scalability, making it a cost-effective alternative to traditional training methods. Health institutions are encouraged to invest in VR as it not only meets the need for innovative educational solutions but also aligns with future trends in medical training, fostering an environment of continuous learning and improvement within the healthcare sector.