Clinical Simulation in Nursing has emerged as a pivotal component of nursing education, revolutionizing the way aspiring nurses acquire practical skills and clinical judgement. According to Dr. Linda A. Smith, a leading expert in the field, “Clinical simulations provide a safe and controlled environment for students to engage in realistic scenarios, bridging the gap between theory and practice.” This approach not only enhances learner engagement but also instills confidence in their ability to perform in actual clinical settings.
In an era where healthcare demands highly skilled professionals, utilizing advanced simulation techniques is essential. From high-fidelity simulators to virtual reality environments, these tools offer nursing students the opportunity to practice critical thinking and decision-making while honing their technical skills. As we delve into the top 10 clinical simulation techniques in nursing education, we will explore how these innovative methods can transform the learning experience, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and preparedness in the nursing workforce. By integrating simulation exercises into the curriculum, educators are equipping future nurses with the proficiency needed to tackle the complexities of modern medicine.
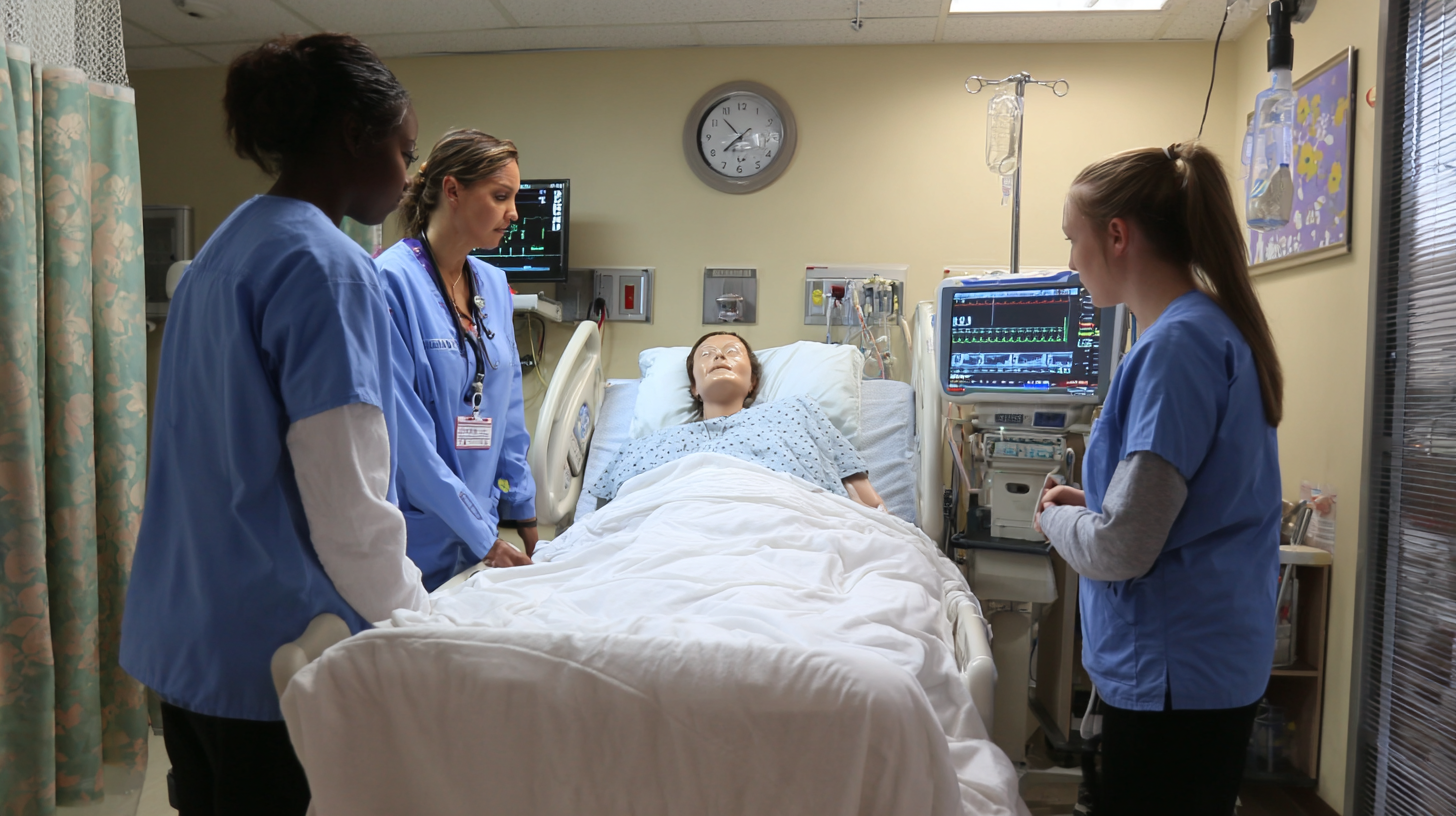

Clinical simulation in nursing education is a transformative approach that enhances essential skills and prepares future nurses for real-world challenges. By engaging in realistic patient scenarios, nursing students can develop critical thinking and decision-making skills without risking patient safety. Here are some top simulation techniques that educators should integrate into their curricula to enhance nursing skills effectively.
One effective technique is high-fidelity simulation, which uses advanced technology and realistic mannequins to mimic actual clinical situations. This method promotes active learning through hands-on experiences, allowing students to practice and refine their skills in a safe environment. Tips for maximizing high-fidelity simulation include pre-briefing sessions to set learning objectives and debriefing afterward to reflect on the experience and identify areas for improvement.
Another valuable technique is standardized patients—actors trained to present clinical cases. This method helps students learn effective communication, empathy, and bedside manner. Tips for utilizing standardized patients effectively include clear guidelines for student interactions and providing constructive feedback to enhance their interpersonal skills. By implementing these innovative simulation techniques, nursing education can produce well-rounded practitioners eager to provide excellent patient care.
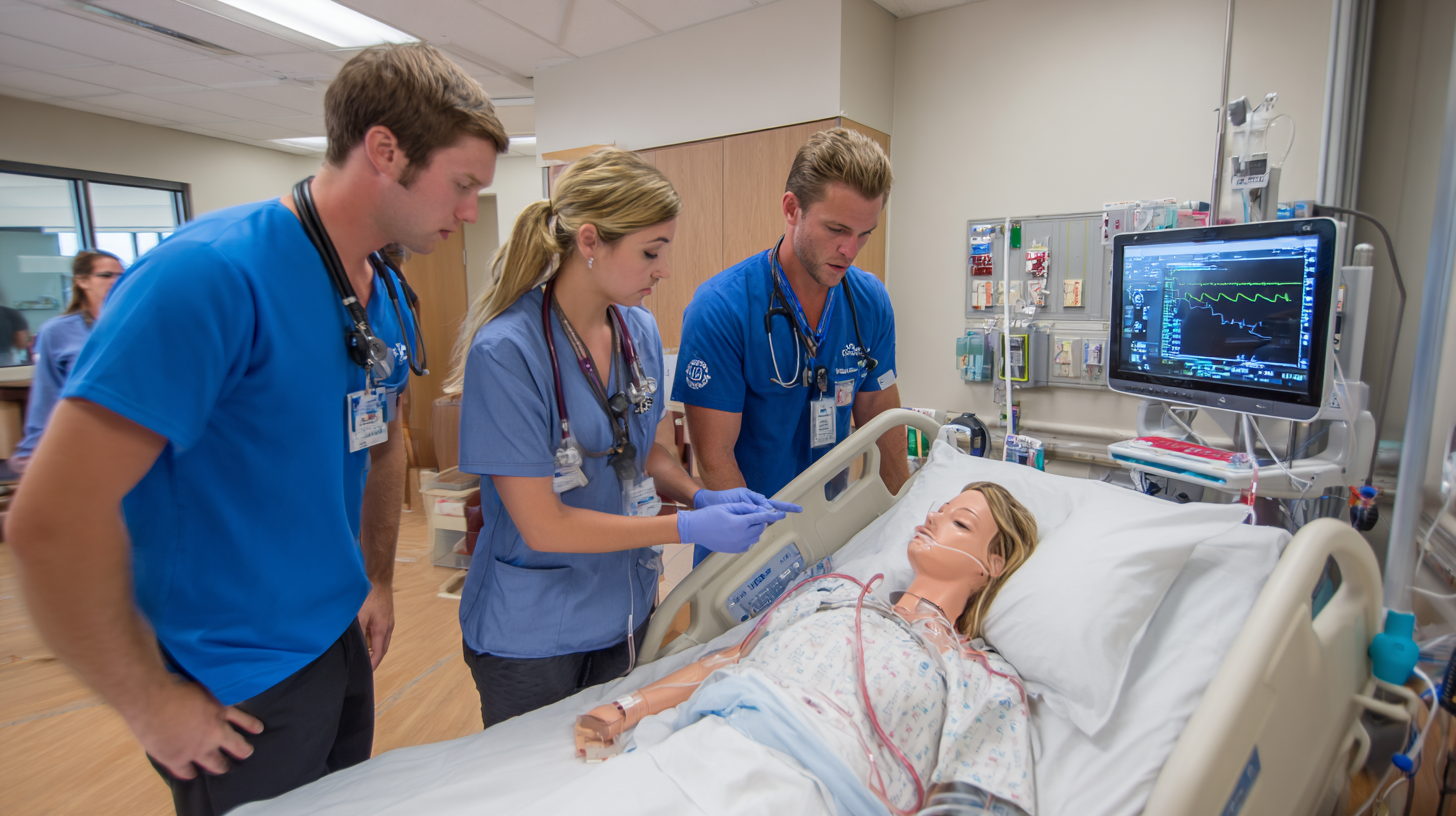

Role-playing as a training tool in nursing education has gained recognition for its effectiveness in enhancing student engagement and preparing them for real-world scenarios. According to a study published in the *International Journal of Nursing Education*, experiential learning techniques, such as role-playing, significantly improve critical thinking skills among nursing students by up to 30%. This technique allows students to immerse themselves in various clinical situations, encouraging them to develop both clinical skills and empathy, which are essential for patient care.
Innovative role-playing methods can be designed to simulate emergencies, patient interactions, and interdisciplinary communication, providing a comprehensive learning experience. Research from the *Nursing Research and Practice* journal indicates that students who engage in role-playing gain 15% more confidence in their clinical abilities compared to traditional teaching methods. These dynamic simulations not only make learning interactive but also foster teamwork and collaboration, vital attributes for nursing professionals in fast-paced environments. Implementing these techniques in nursing curricula can lead to higher retention rates and improved patient outcomes in their future practice.
| Simulation Technique | Description | Benefits | Student Engagement Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized Patients | Trained actors simulate real patients to enhance clinical skills. | Improves communication, empathy, and assessment skills. | High |
| High-Fidelity Simulators | Advanced mannequins that mimic real physiological responses. | Allows for realistic practice and immediate feedback. | Very High |
| Virtual Simulation | Online scenarios with interactive cases for remote learning. | Facilitates learning anytime, anywhere; offers flexibility. | Moderate |
| Role-Playing Scenarios | Students take on roles to practice interpersonal skills. | Enhances critical thinking and teamwork abilities. | High |
| Debriefing Sessions | Reflection and discussion following simulations. | Enhances understanding and retention of knowledge. | Moderate |
| Team-Based Learning | Collaborative learning using real-world scenarios. | Promotes collaboration and critical thinking. | High |
| Skills Competency Assessments | Structured evaluations of specific clinical skills. | Ensures proficiency before practice. | Moderate |
| Interprofessional Education | Joint simulation sessions with other healthcare professions. | Fosters teamwork and communication across disciplines. | High |
| Point-of-Care Simulation | Real-time simulations at the bedside in clinical settings. | Provides immediate clinical learning; context-rich. | Very High |
| Case-Based Learning | In-depth analysis of real patient cases to apply knowledge. | Promotes critical thinking and application of skills. | High |
As the landscape of nursing education evolves, realistic virtual simulations have emerged as a game-changing method for training future healthcare professionals. According to a report by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN), the integration of simulation into nursing curricula can enhance learner outcomes, with studies showing that students who participated in high-fidelity simulations scored higher on clinical competency assessments than their peers receiving traditional training. This significant shift underscores the potential of technology to provide immersive, engaging, and effective learning experiences that prepare nurses for real-world challenges.
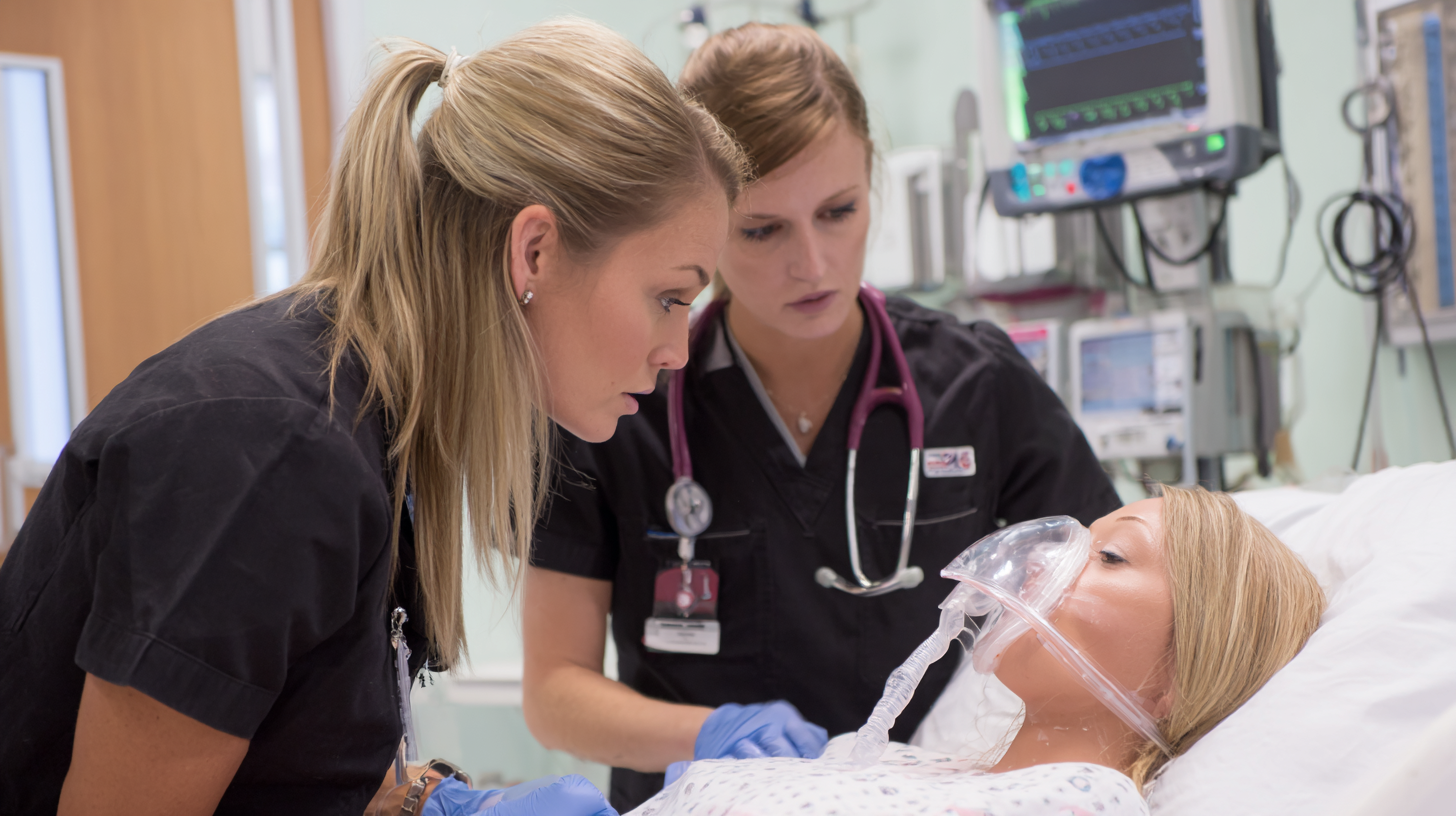

Furthermore, a recent survey by the American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN) revealed that 80% of nursing schools have incorporated simulation-based learning, with many institutions reporting improvements in student confidence and preparedness. Virtual simulations offer a safe environment for students to practice critical thinking and decision-making skills without risking patient safety. By recreating high-pressure clinical scenarios, students can hone their abilities in a controlled setting, making them more capable and confident when they enter the workforce. As nursing education continues to embrace these innovative techniques, the future of nursing training looks brighter than ever.
Effective debriefing techniques are crucial in maximizing learning outcomes in clinical simulation for nursing education. Research indicates that structured debriefing can enhance critical thinking skills by up to 22%, helping students to reflect on their performance and integrate theoretical knowledge with practical experience (Lavoie et al., 2020). In a simulated environment, debriefing creates a safe space for learners to discuss what they did well and identify areas for improvement. This process not only solidifies learning but also fosters a deeper understanding of clinical concepts.
Furthermore, incorporating elements of psychological safety during debriefing sessions significantly influences participant engagement and retention of knowledge. A study by Cant and Cooper (2017) showed that when learners felt safe to articulate their thoughts and experiences, retention of information improved by 30%. Effective debriefing should utilize open-ended questions, encouraging reflective dialogue and allowing learners to construct their knowledge. By focusing on these evidenced-based techniques, nursing educators can greatly enhance the impact of simulation experiences, ultimately leading to better prepared future nurses.
Interprofessional collaboration is essential in nursing education, particularly through the lens of clinical simulations. Recent partnership initiatives demonstrated how interprofessional educational (IPE) interventions can significantly enhance collaboration skills among nursing and medical students. For instance, studies indicate that classroom-based IPE not only fosters teamwork but also sustains collaboration skills long-term, benefiting students in real-life clinical settings. Reinacting real-life scenarios allows nursing students to engage with peers from various health disciplines, ultimately promoting a holistic approach to patient care.
Incorporating interprofessional simulations in nursing curricula can enhance learning experiences and prepare students for collaborative practice. As shown in simulation events, students practicing side by side can effectively navigate complex patient cases, leading to improved clinical reasoning and communication skills. Tips for maximizing interprofessional collaboration in simulations include creating a supportive environment, ensuring clear role definitions for each discipline, and providing debriefing sessions to reflect on team dynamics.
Furthermore, technology-rich nursing simulation centers are revolutionizing healthcare education. By integrating classroom knowledge with practical skills through simulations, students gain valuable experience that directly translates to their future clinical roles. Emphasizing interprofessional experiences can significantly enrich nursing education, ultimately leading to higher quality patient care in diverse healthcare settings.